
It fetches and merges changes from the remote server to your working directory. You can also set it with a push git push -u origin master git push -set-upstream origin master Branch branchName set up to track remote branch branchName from origin. You update/set an upstream with the branch command. git branch -u origin/branchName # or git branch -set-upstream-to=origin/master master To push your changes into your remote repo, execute the git push command:Ĥ.
you can use any name instead of "origin".For example: #set a new remote Two ways, 1.git remote add my_awesome_new_remote_repo # or 2.git remote add origin #Verify new remote git remote -v > my_awesome_new_remote_repo (fetch) my_awesome_new_remote_repo (push) origin (fetch) origin (push) "origin" is the local name of the remote repository.
#Git add remote url to local repository mac#
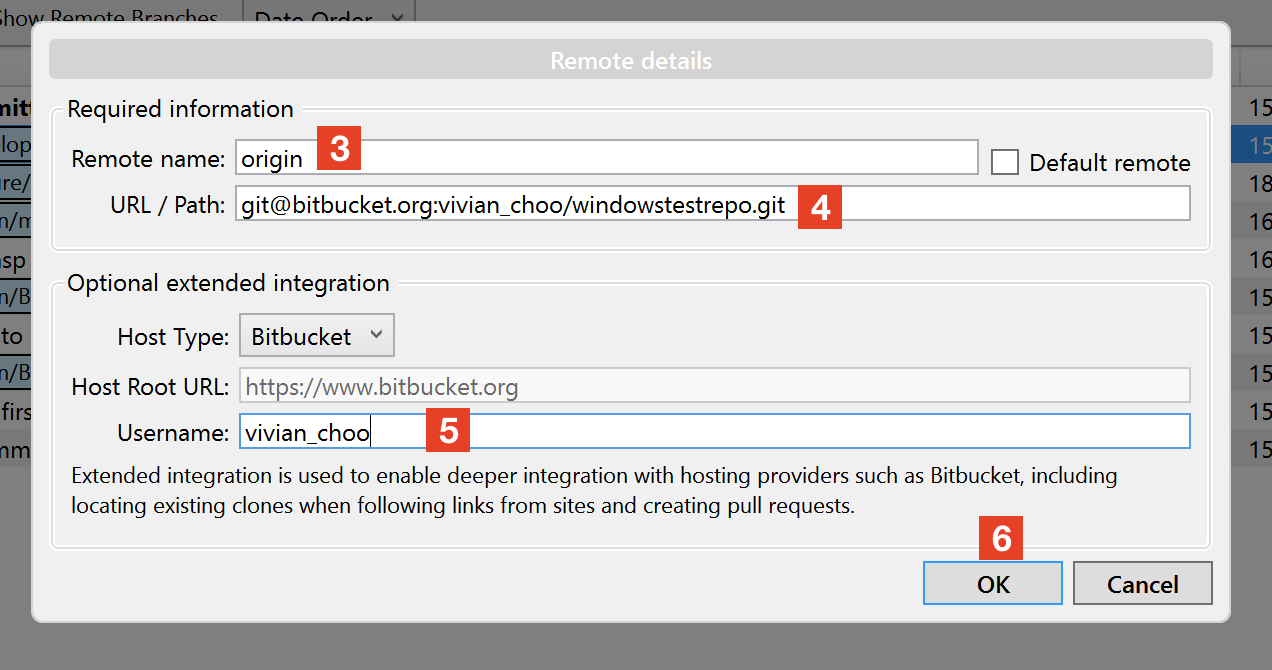
Note: "origin" is a convention not part of the command. I am trying to set up a remote repository on a Mac on my local network. You can verify that the remote URL has changed, with command git remote -v. For example, origin or upstream are two common choices.įor example you can change your remote's URL from SSH to HTTPS with the git remote set-url command. git init:- This will make the local folder as Git repository, Link the remote branch:- Now challenge is associate the local git repository with remote master branch. Creating local repository:-Initially user may have created the local git repository. The git remote set-url command takes two arguments: Here is the complete process to create a local repo and push the changes to new remote branch. Push a branch to all the remotes with git push all BRANCH replace BRANCH. Register 2 nd push URL: git remote set-url -add -push all REMOTE-URL-2.

Register 1 st push URL: git remote set-url -add -push all REMOTE-URL-1. Say, we call it all: git remote add all REMOTE-URL-1. The git remote set-url command changes an existing remote repository URL. Define a git remote which will point to multiple git remotes.
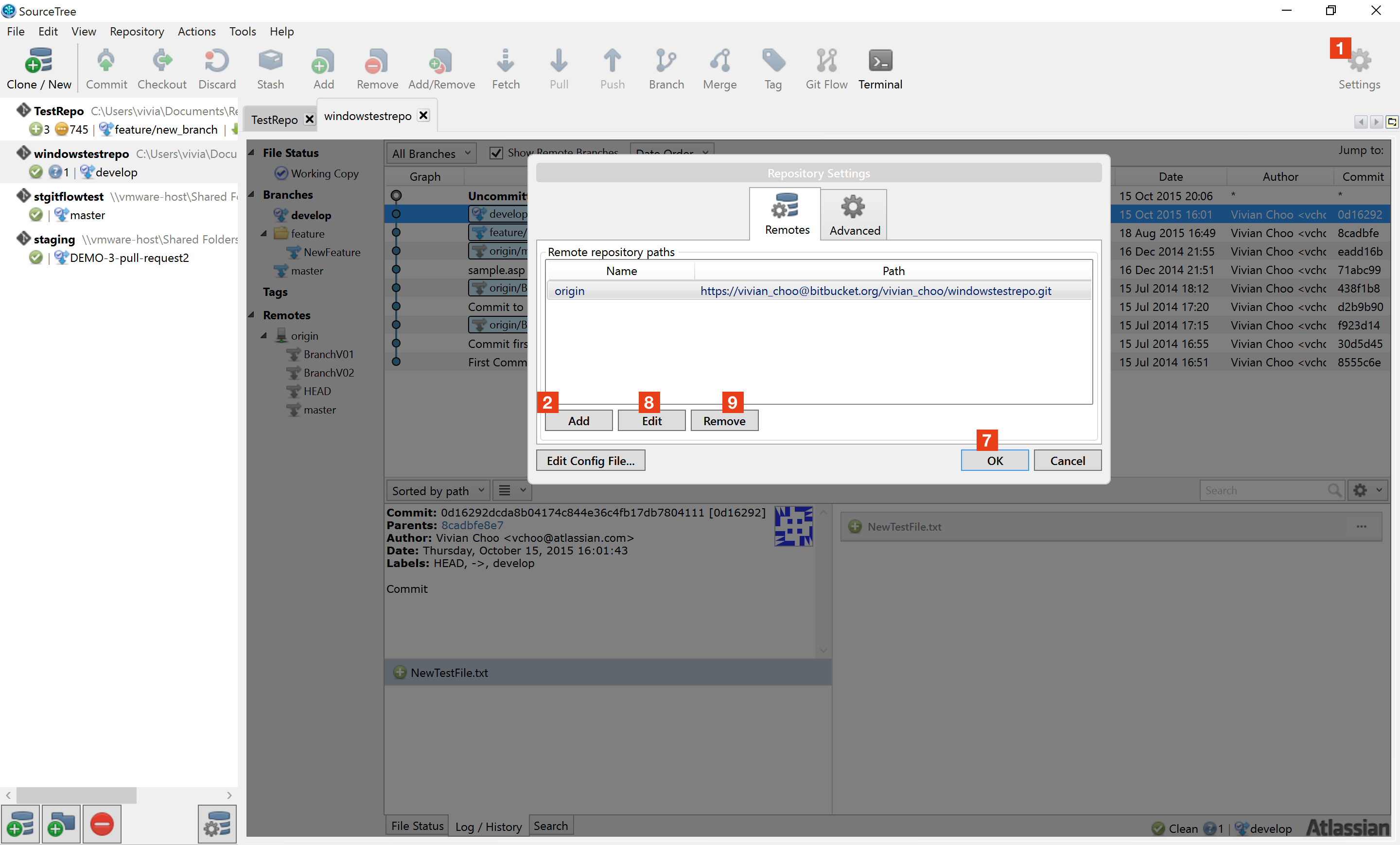
The git remote add command takes two arguments: This command is used to add a new remote, you can use this command on the terminal, in the directory of your repository. 9) Copy remote repository URL field 10) In Terminal, add the URL for the remote repository where your local repository will. 8) At the top of your GitHub repositorys Quick Setup page, click to copy the remote repository URL. git then the repository not exists, so you have to add origin with command git remote add To remove this commit and modify the file, use git reset -soft HEAD1 and commit and add the file again. You can check remote with command git remote -v it will show remote url after name, or if this command gives error like fatal: Not a git repository (or any of the parent directories). So the command git remote set-url will only work if you've either cloned the repository or manually added a remote called origin. Step 3: Adding Remote URL To a Local Repo. In the previous step, we created a new local Git repo. We will need a local Git repo to which we will be adding the new remote. Step 1: Initializing Git in Your Project. You can not call remote set-url origin just after git init, Because the git remote set-url command will not create origin, but it changes an existing remote repository URL. This post assumes that you already have Git installed on your local machine. To know about the list of all branches you have in your repository type : git branch This command simply pushes your files to the remote repository.Git has a concept of something known as a "branch", so by default everything is pushed to the master branch unless explicitly specified an alternate branch. git remote set-url origin command means that if at any stage you wish to change the location of your repository(i.e if you made a mistake while adding the remote path using the git add command) the first time, you can easily go back & "reset(update) your current remote repository path" by using the above command. When you clone a repository with git clone, it automatically creates a remote connection called origin pointing back to the cloned repository. To verify that the remote is set properly type : git remote -vĢ.Here origin is an alias/alternate name for your remote repository so that you don't have to type the entire path for remote every time and henceforth you are declaring that you will use this name(origin) to refer to your remote.Your remote repository could be anywhere on github, gitlab, bitbucket, etc.This command simply means "you are adding the location of your remote repository where you wish to push/pull your files to/from !!.".
#Git add remote url to local repository series#
git remote add origin This command is the second step in the command series after you initialize git into your current working repository using git init.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
